Critical Surface Tension and Contact Angle with Water for Various Polymers
ID #(1)
  |
Polymer Name(2)
  |
CAS #(3)
  |
γS(4)
  |
Contact Angle(5)
  |
| 6 |
Nylon 6,6
|
32131-17-2 |
42.2 |
68.3 |
| 27 |
Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS)
|
26125-40-6 |
38 |
80.3 |
| 15 |
Poly n-butyl methacrylate (PnBMA)
|
25608-33-7 |
29.8 |
91 |
| 11 |
Nylon 11
|
25587-80-8 |
35.6 |
82 |
| 21 |
Polyethylene oxide (PEO, PEG, polyethylene glycol)
|
25322-68-3 |
43 |
63 |
| 34 |
Polyvinyl alcohol (PVOH)
|
25213-24-5 |
37 |
51 |
| 16 |
Poly t-butyl methacrylate (PtBMA)
|
25189-00-9 |
18.1 |
108.1 |
| 30 |
Polysulfone (PSU)
|
25135-51-7 |
42.1 |
70.5 |
| 3 |
Fluorinated ethylene propylene (FEP)
|
25067-11-2 |
19.1 |
108.5 |
| 22 |
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET)
|
25038-59-9 |
39 |
72.5 |
| 5 |
Nylon 6 (polycaprolactum, aramid 6)
|
25038-54-4 |
43.9 |
62.6 |
| 36 |
Polyvinyl fluoride (PVF)
|
24981-14-4 |
32.7 |
84.5 |
| 32 |
Polytrifluoroethylene
|
24980-67-4 |
26.5 |
92 |
| 26 |
Polyoxymethylene (POM, polyacetal, polymethylene oxide)
|
24969-26-4 |
37 |
76.8 |
| 38 |
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF)
|
24937-79-9 |
31.6 |
89 |
| 12 |
Nylon 12
|
24937-16-4 |
37.1 |
72.4 |
| 17 |
Polycarbonate (PC)
|
24936-68-3 |
44 |
82 |
| 19 |
Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS)
|
9016-00-6 |
20.1 |
107.2 |
| 25 |
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA, acrylic, plexiglas)
|
9011-14-7 |
37.5 |
70.9 |
| 1 |
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS)
|
9003-56-9 |
38.5 |
80.9 |
| 29 |
Polystyrene (PS)
|
9003-53-6 |
34 |
87.4 |
| 24 |
Polyisobutylene (PIB, butyl rubber)
|
9003-27-4 |
27 |
112.1 |
| 33 |
Polyvinyl acetate (PVA)
|
9003-20-7 |
35.3 |
60.6 |
| 14 |
Polybutadiene
|
9003-17-2 |
29.3 |
96 |
| 20 |
Polyethylene (PE)
|
9002-88-4 |
31.6 |
96 |
| 35 |
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC)
|
9002-86-2 |
37.9 |
85.6 |
| 37 |
Polyvinylidene chloride (PVDC, Saran)
|
9002-85-1 |
40.2 |
80 |
| 31 |
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)
|
9002-84-0 |
19.4 |
109.2 |
| 18 |
Polychlorotrifluoroethylene (PCTFE)
|
9002-83-9 |
30.8 |
99.3 |
| 13 |
Paraffin
|
8002-74-2 |
24.8 |
108.9 |
| 4 |
Hexatriacontane
|
630-06-8 |
20.6 |
108.5 |
| 28 |
Polypropylene (PP)
|
(a) |
30.5 |
102.1 |
| 23 |
Poly(hexafluoropropylene)
|
- |
16.9 |
112 |
| 10 |
Nylon 10,10
|
- |
32 |
94 |
| 9 |
Nylon 9,9
|
- |
34 |
86 |
| 8 |
Nylon 8,8
|
- |
34 |
86 |
| 7 |
Nylon 7,7
|
- |
43 |
70 |
| 2 |
Epoxies
|
- |
44.5 |
76.3 |
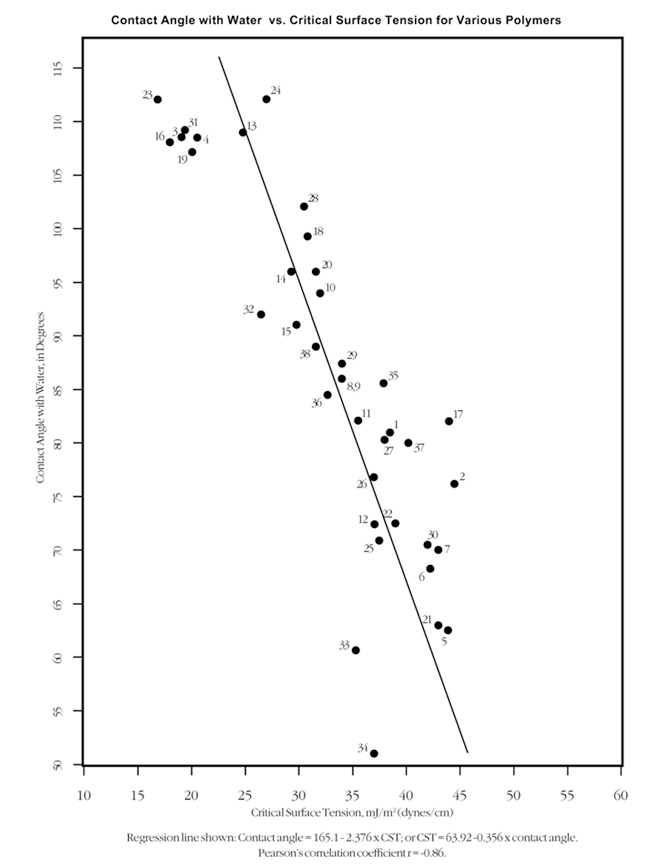
(1) ID numbers identify polymer data points in critical surface tension vs. contact angle chart.
(2) Names which are most widely used to describe the material or family of materials (e.g., polyurethanes and epoxies) at
hand are preferred here. Commonly used acronyms and synonyms are also shown. 
(3) CAS (Chemical Abstract Series) numbers are shown where available. In a number of instances, more than one CAS
number is assigned to a given polymer — in some cases the details and nuances of these divergences are not at all clear. We
have tried to reference the CAS number which appears to have the widest use with reference to the solid state properties of
the given polymer . 
(4) Critical surface tension in
mJ/m2 (equivalent to dynes/cm), generally determined by the Zisman method (regression of
the cosine of the contact angle), or by the wetting tension method (using solutions of 2-ethoxyethanol and formamide,
per ASTM Std. D-2578). 
(5) Contact angle with water, in degrees. The arithmetic mean of all equilibrium (Young's) and advancing contact
angle measurements is shown. Generally, the equilibrium angle is similar to, but slightly lower than, the advancing angle;
the balance of equilibrium vs. advancing contact angles from which this summary is drawn may have some effect on
the average as shown for some polymers. 
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
